Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
The Benefits of Kernel PCovR for the WHO Dataset#
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import pearsonr
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA, KernelPCA
from sklearn.kernel_ridge import KernelRidge
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge, RidgeCV
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, train_test_split
from skmatter.datasets import load_who_dataset
from skmatter.decomposition import KernelPCovR, PCovR
from skmatter.preprocessing import StandardFlexibleScaler
Load the Dataset#
df = load_who_dataset()["data"]
print(df)
Country Year ... SN.ITK.DEFC.ZS NY.GDP.PCAP.CD
0 Afghanistan 2005 ... 36.1 255.055120
1 Afghanistan 2006 ... 33.3 274.000486
2 Afghanistan 2007 ... 29.8 375.078128
3 Afghanistan 2008 ... 26.5 387.849174
4 Afghanistan 2009 ... 23.3 443.845151
... ... ... ... ... ...
2015 South Africa 2015 ... 5.2 6204.929901
2016 South Africa 2016 ... 5.4 5735.066787
2017 South Africa 2017 ... 5.5 6734.475153
2018 South Africa 2018 ... 5.7 7048.522211
2019 South Africa 2019 ... 6.3 6688.787271
[2020 rows x 12 columns]
Below, we take the logarithm of the population and GDP to avoid extreme distributions
log_scaled = ["SP.POP.TOTL", "NY.GDP.PCAP.CD"]
for ls in log_scaled:
print(X_raw[:, columns.index(ls)].min(), X_raw[:, columns.index(ls)].max())
if ls in columns:
X_raw[:, columns.index(ls)] = np.log10(X_raw[:, columns.index(ls)])
y_raw = np.array(df["SP.DYN.LE00.IN"])
y_raw = y_raw.reshape(-1, 1)
X_raw.shape
149841.0 7742681934.0
110.460874721483 123678.70214327476
(2020, 9)
Scale and Center the Features and Targets#
x_scaler = StandardFlexibleScaler(column_wise=True)
X = x_scaler.fit_transform(X_raw)
y_scaler = StandardFlexibleScaler(column_wise=True)
y = y_scaler.fit_transform(y_raw)
n_components = 2
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, random_state=0
)
Train the Different Linear DR Techniques#
Below, we obtain the regression errors using a variety of linear DR techniques.
Linear Regression#
0.8548848257886271
PCovR#
pcovr = PCovR(
n_components=n_components,
regressor=Ridge(alpha=1e-4, fit_intercept=False),
mixing=0.5,
random_state=0,
).fit(X_train, y_train)
T_train_pcovr = pcovr.transform(X_train)
T_test_pcovr = pcovr.transform(X_test)
T_pcovr = pcovr.transform(X)
r_pcovr = Ridge(alpha=1e-4, fit_intercept=False, random_state=0).fit(
T_train_pcovr, y_train
)
yp_pcovr = r_pcovr.predict(T_test_pcovr).reshape(-1, 1)
plt.scatter(y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_test), y_scaler.inverse_transform(yp_pcovr))
r_pcovr.score(T_test_pcovr, y_test)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/scikit-matter/envs/257/lib/python3.13/site-packages/skmatter/decomposition/_pcov.py:50: UserWarning: This class does not automatically center data, and your data mean is greater than the supplied tolerance.
warnings.warn(
0.8267220275787428
PCA#
pca = PCA(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=0,
).fit(X_train, y_train)
T_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train)
T_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test)
T_pca = pca.transform(X)
r_pca = Ridge(alpha=1e-4, fit_intercept=False, random_state=0).fit(T_train_pca, y_train)
yp_pca = r_pca.predict(T_test_pca).reshape(-1, 1)
plt.scatter(y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_test), y_scaler.inverse_transform(yp_pca))
r_pca.score(T_test_pca, y_test)
0.8041174131375703
SP.POP.TOTL -0.22694404485361055 -0.3777743593940685
SH.TBS.INCD -0.6249287177098704 0.6316215151702456
SH.IMM.MEAS 0.842586228381343 0.13606904827472627
SE.XPD.TOTL.GD.ZS 0.41457342404840136 0.6100854823971251
SH.DYN.AIDS.ZS -0.3260933054303097 0.8499296260662148
SH.IMM.IDPT 0.8422637385674645 0.16339769662915174
SH.XPD.CHEX.GD.ZS 0.45900120895545243 0.30686303937881865
SN.ITK.DEFC.ZS -0.8212324937958553 0.055108835843951376
NY.GDP.PCAP.CD 0.8042167907410392 0.06566227478694868
Train the Different Kernel DR Techniques#
Below, we obtain the regression errors using a variety of kernel DR techniques.
Select Kernel Hyperparameters#
In the original publication, we used a cross-validated grid search to determine the
best hyperparameters for the kernel ridge regression. We do not rerun this expensive
search in this example but use the obtained parameters for gamma and alpha.
You may rerun the calculation locally by setting recalc=True.
recalc = False
if recalc:
param_grid = {"gamma": np.logspace(-8, 3, 20), "alpha": np.logspace(-8, 3, 20)}
clf = KernelRidge(kernel="rbf")
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=clf, param_grid=param_grid)
gs.fit(X_train, y_train)
gamma = gs.best_estimator_.gamma
alpha = gs.best_estimator_.alpha
else:
gamma = 0.08858667904100832
alpha = 0.0016237767391887243
kernel_params = {"kernel": "rbf", "gamma": gamma}
Kernel Regression#
KernelRidge(**kernel_params, alpha=alpha).fit(X_train, y_train).score(X_test, y_test)
0.9726524136785997
KPCovR#
kpcovr = KernelPCovR(
n_components=n_components,
regressor=KernelRidge(alpha=alpha, **kernel_params),
mixing=0.5,
**kernel_params,
).fit(X_train, y_train)
T_train_kpcovr = kpcovr.transform(X_train)
T_test_kpcovr = kpcovr.transform(X_test)
T_kpcovr = kpcovr.transform(X)
r_kpcovr = KernelRidge(**kernel_params).fit(T_train_kpcovr, y_train)
yp_kpcovr = r_kpcovr.predict(T_test_kpcovr)
plt.scatter(y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_test), y_scaler.inverse_transform(yp_kpcovr))
r_kpcovr.score(T_test_kpcovr, y_test)
0.9701003539460163
KPCA#
kpca = KernelPCA(n_components=n_components, **kernel_params, random_state=0).fit(
X_train, y_train
)
T_train_kpca = kpca.transform(X_train)
T_test_kpca = kpca.transform(X_test)
T_kpca = kpca.transform(X)
r_kpca = KernelRidge(**kernel_params).fit(T_train_kpca, y_train)
yp_kpca = r_kpca.predict(T_test_kpca)
plt.scatter(y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_test), y_scaler.inverse_transform(yp_kpca))
r_kpca.score(T_test_kpca, y_test)
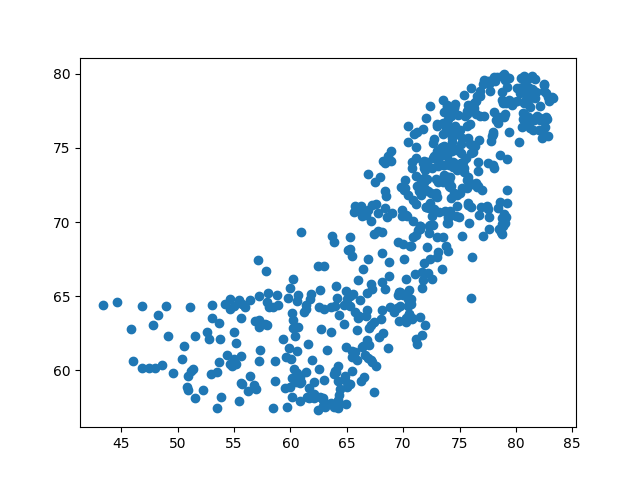
0.6661226058827727
Correlation of the different variables with the KPCovR axes#
SP.POP.TOTL 0.07320109486755187 0.03969226130174684
SH.TBS.INCD 0.6836177728806814 -0.05384746771432407
SH.IMM.MEAS -0.6604939713030802 0.047519698518210675
SE.XPD.TOTL.GD.ZS -0.23009788930020397 -0.3622748865999962
SH.DYN.AIDS.ZS 0.5157981075022208 -0.1170132700029201
SH.IMM.IDPT -0.6449500965012953 0.05262226781868083
SH.XPD.CHEX.GD.ZS -0.38019935560127377 -0.5736426627623917
SN.ITK.DEFC.ZS 0.7301250686596462 0.04793454286747634
NY.GDP.PCAP.CD -0.82286600973303 -0.49386365697113266
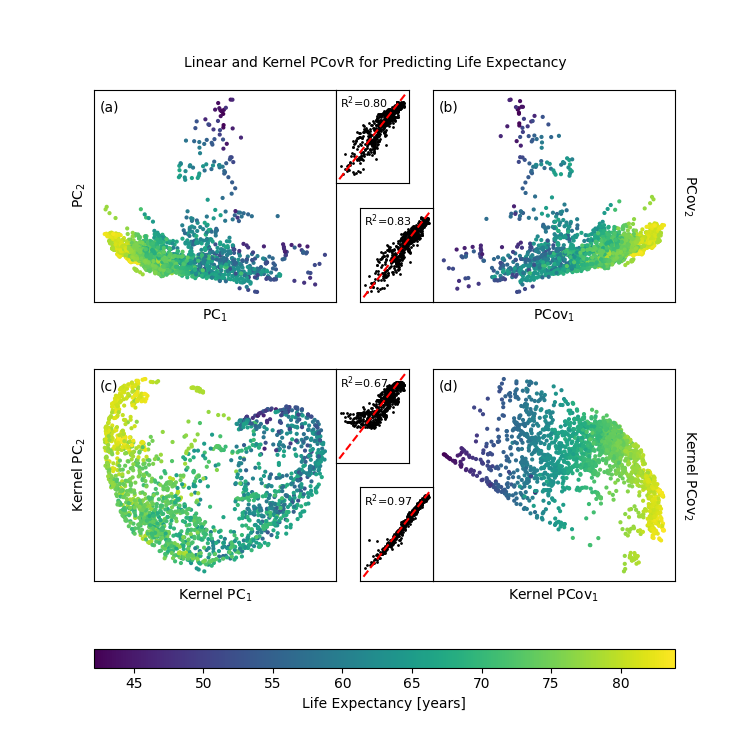
Plot Our Results#
fig, axes = plt.subplot_mosaic(
"""
AFF.B
A.GGB
.....
CHH.D
C.IID
.....
EEEEE
""",
figsize=(7.5, 7.5),
gridspec_kw=dict(
height_ratios=(0.5, 0.5, 0.1, 0.5, 0.5, 0.1, 0.1),
width_ratios=(1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.1, 1),
),
)
axPCA, axPCovR, axKPCA, axKPCovR = axes["A"], axes["B"], axes["C"], axes["D"]
axPCAy, axPCovRy, axKPCAy, axKPCovRy = axes["F"], axes["G"], axes["H"], axes["I"]
def add_subplot(ax, axy, T, yp, let=""):
"""Adding a subplot to a given axis."""
p = ax.scatter(-T[:, 0], T[:, 1], c=y_raw, s=4)
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.annotate(
xy=(0.025, 0.95), xycoords="axes fraction", text=f"({let})", va="top", ha="left"
)
axy.scatter(
y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_test),
y_scaler.inverse_transform(yp),
c="k",
s=1,
)
axy.plot([y_raw.min(), y_raw.max()], [y_raw.min(), y_raw.max()], "r--")
axy.annotate(
xy=(0.05, 0.95),
xycoords="axes fraction",
text=r"R$^2$=%0.2f" % round(r2_score(y_test, yp), 3),
va="top",
ha="left",
fontsize=8,
)
axy.set_xticks([])
axy.set_yticks([])
return p
p = add_subplot(axPCA, axPCAy, T_pca, yp_pca, "a")
axPCA.set_xlabel("PC$_1$")
axPCA.set_ylabel("PC$_2$")
add_subplot(axPCovR, axPCovRy, T_pcovr @ np.diag([-1, 1]), yp_pcovr, "b")
axPCovR.yaxis.set_label_position("right")
axPCovR.set_xlabel("PCov$_1$")
axPCovR.set_ylabel("PCov$_2$", rotation=-90, va="bottom")
add_subplot(axKPCA, axKPCAy, T_kpca @ np.diag([-1, 1]), yp_kpca, "c")
axKPCA.set_xlabel("Kernel PC$_1$", fontsize=10)
axKPCA.set_ylabel("Kernel PC$_2$", fontsize=10)
add_subplot(axKPCovR, axKPCovRy, T_kpcovr, yp_kpcovr, "d")
axKPCovR.yaxis.set_label_position("right")
axKPCovR.set_xlabel("Kernel PCov$_1$", fontsize=10)
axKPCovR.set_ylabel("Kernel PCov$_2$", rotation=-90, va="bottom", fontsize=10)
plt.colorbar(
p, cax=axes["E"], label="Life Expectancy [years]", orientation="horizontal"
)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0, hspace=0.4)
fig.suptitle(
"Linear and Kernel PCovR for Predicting Life Expectancy", y=0.925, fontsize=10
)
plt.show()